How Solar Power Works
How Solar Power Works
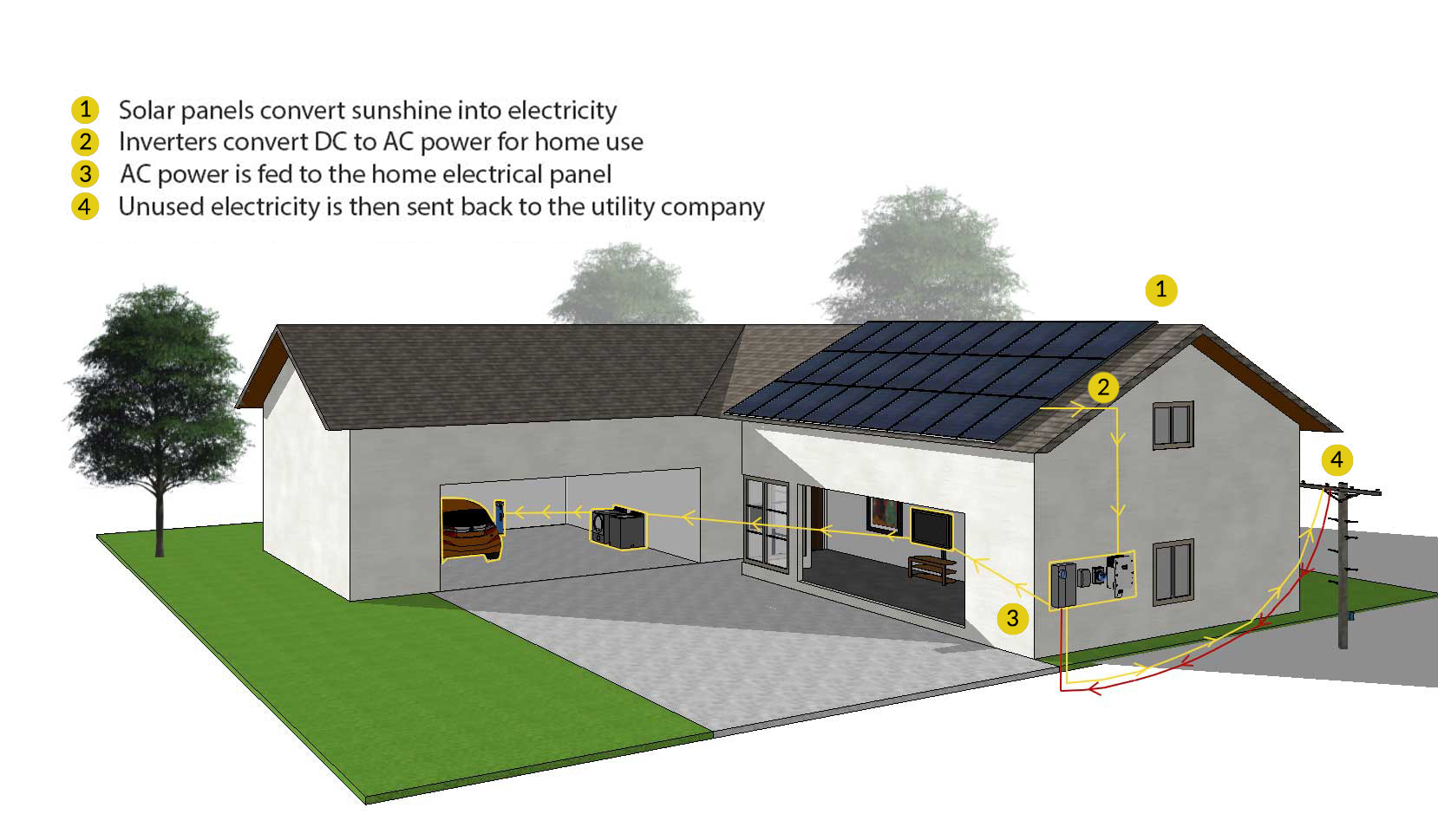
How A Solar Power Systems Works

Solar Panels
Solar panels absorb photons from the sun and convert them into Direct Current (DC) electricity which flows to an inverter.

Solar Panels
Solar panels absorb photons from the sun and convert them into Direct Current (DC) electricity which flows to an inverter.

Solar Panels
Solar panels absorb photons from the sun and convert them into Direct Current (DC) electricity which flows to an inverter.

Solar Panels
Solar panels absorb photons from the sun and convert them into Direct Current (DC) electricity which flows to an inverter.
Considering Solar? Let's Talk
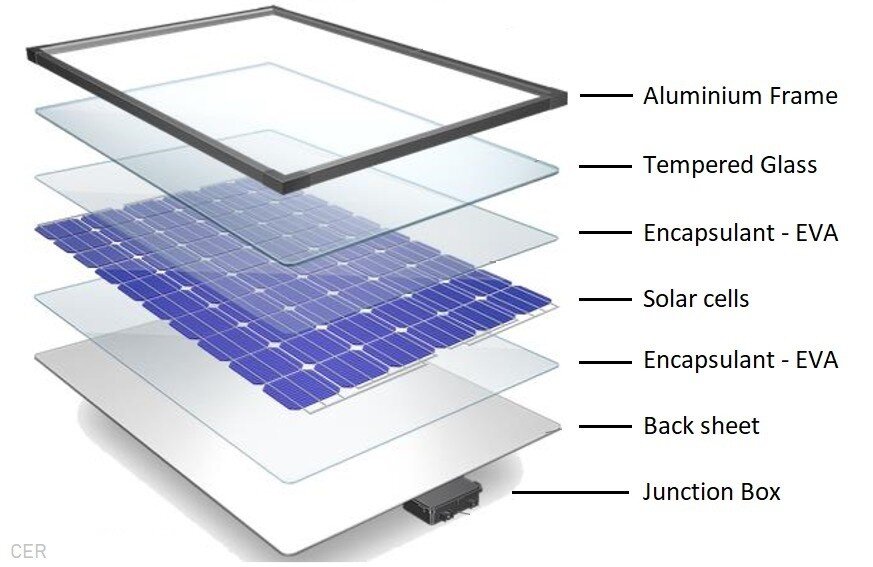
What Solar Panels Are Made Of
Solar modules, also known as solar panels, are made up of a solid layer of silicon cells, electrical wiring, a metal frame, and a glass casing to contain their complex structure. Silicon, the chemical element that composes the solar cells, is represented by the symbol Si and atomic number 14 of the periodic table right below carbon and above the tin, lead, and germanium. Silicon-based solar panels hold conductive properties that absorb photons from the sun and convert them into reusable electricity. The electrons in the silicon cell are set free from their atoms to respond to sunlight. The photovoltaic effect is then triggered, providing the electric current, which is the basis for your solar energy production.
After the solar panels capture the electrical charge from the sun, that energy needs to be harnessed and redirected to power your home effectively. You will then need an inverter to convert the direct current (DC) captured by the solar panels into alternating currents (AC). Ultimately, the inverter redirects the electricity supply to each outlet in your home, allowing the solar panels to effectively replace the utility grid as your primary, or even your sole, power generation source.
